| PHOSPHORYLATION OF ERK/MAP KINASE IS REQUIRED FOR
LTP AT THALAMIC AND CORTICAL INPUTS TO THE LATERAL AMYGDALA IN
VIVO |
| G.E.Schafe1*; M.W.Swank2;
S.M.Rodrigues3; J.E.LeDoux3; V.Doyere4
|
| 1. Psychology, Yale Univ., New Haven, CT, USA |
| 2. Baylor Col. of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA |
| 3. Center for Neural Science, NYU, New York, NY, USA |
| 4. Univ. Paris Sud, Orsay, France |
|
The present experiments examined the role of ERK/MAPK
at thalamic and cortical inputs to the LA, in vivo. First,
we used immunohistochemistry and Western blotting methods to examine
the regulation of ERK/MAPK following LTP in the LA. Anesthetized rats
were implanted with a bipolar stimulating electrode into either the
auditory thalamus (MGm/PIN) or auditory cortex (area TE3) and given
LTP-inducing high frequency stimulation (HFS, 3 theta-patterned 100
Hz tetani, 300 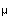 A,
100 A,
100 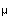 sec).
Controls received the same number of pulses over the same time period
(2 min), but at low frequency (LFS; 2.5 Hz). Results showed that HFS,
but not LFS, led to significant activation of ERK/MAPK in the LA;
the total amount of ERK protein was not affected. This activation
was anatomically restricted: ERK-labeled cells were observed primarily
in the ventral LAd and the LAvl, as well as the ventral striatum (CPu)
and nearby amygdala striatal transition zone (AST), but not in the
basal nucleus of the amygdala. In a second set of experiments, we
examined whether activation of ERK/MAPK was necessary for LTP. Rats
received either HFS or LFS 1 Hr following systemic administration
of either vehicle (DMSO; 0.3 ml; i.p.) or the MEK inhibitor SL327
(75 mg/kg; i.p.). Relative to controls, SL327 impaired the activation
of ERK/MAPK following HFS, and also impaired LTP at both thalamic
and cortical inputs to the LA. SL327 did not significantly affect
baseline transmission in either pathway. In a final experiment, we
examined the effect of local intra-LA infusion of the MEK inhibitor
U0126 on LTP at thalamic inputs to the LA. Local infusion of U0126
(1 sec).
Controls received the same number of pulses over the same time period
(2 min), but at low frequency (LFS; 2.5 Hz). Results showed that HFS,
but not LFS, led to significant activation of ERK/MAPK in the LA;
the total amount of ERK protein was not affected. This activation
was anatomically restricted: ERK-labeled cells were observed primarily
in the ventral LAd and the LAvl, as well as the ventral striatum (CPu)
and nearby amygdala striatal transition zone (AST), but not in the
basal nucleus of the amygdala. In a second set of experiments, we
examined whether activation of ERK/MAPK was necessary for LTP. Rats
received either HFS or LFS 1 Hr following systemic administration
of either vehicle (DMSO; 0.3 ml; i.p.) or the MEK inhibitor SL327
(75 mg/kg; i.p.). Relative to controls, SL327 impaired the activation
of ERK/MAPK following HFS, and also impaired LTP at both thalamic
and cortical inputs to the LA. SL327 did not significantly affect
baseline transmission in either pathway. In a final experiment, we
examined the effect of local intra-LA infusion of the MEK inhibitor
U0126 on LTP at thalamic inputs to the LA. Local infusion of U0126
(1 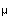 g)
blocked LTP at thalamic inputs, without affecting routine transmission.
Thus, activation of ERK/MAPK is required for LTP at thalamic and cortical
inputs to the LA, in vivo. g)
blocked LTP at thalamic inputs, without affecting routine transmission.
Thus, activation of ERK/MAPK is required for LTP at thalamic and cortical
inputs to the LA, in vivo.
Support Contributed By: MH46516 to J.E.L., MH62519 to G.E.S. and
CNRS-NSF17089 (to V.D.).
|
Program No. 415.2
Poster presentation:Monday, Nov. 14, 11:00 AM - 12:00 PM
Location: HH25 |
|
|
|